Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Coughs, Age 12 and Older
Overview
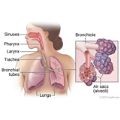
Coughing is the body's way of removing foreign material or mucus from the lungs and upper airway passages or of reacting to an irritated airway.
Coughs have certain traits you can learn to recognize. A cough is only a symptom, not a disease. Often, you can't tell how serious the problem is until you also look at the other symptoms.
Productive coughs
A productive cough produces phlegm or mucus (sputum). The mucus may have drained down the back of the throat from the nose or sinuses. Or it may have come up from the lungs. In most cases, you shouldn't suppress a productive cough. The cough clears mucus from the lungs. There are many causes of a productive cough, such as:
- Viral illnesses. It's normal to have a productive cough when you have a common cold. Coughing is often triggered by mucus that drains down the back of the throat.
- Infections. An infection of the lungs or upper airway passages can cause a cough. A productive cough may be a symptom of pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis, or tuberculosis.
- Chronic lung disease. A productive cough could be a sign that a disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is getting worse or that you have an infection.
- Stomach acid backing up into the esophagus. This type of coughing may be a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It may awaken you from sleep.
- Nasal discharge (postnasal drip) draining down the back of the throat. This can cause a productive cough or the feeling that you constantly need to clear your throat. Experts disagree about whether a postnasal drip or the viral illness that caused it is causing the cough.
- Smoking or other tobacco use. Productive coughs in a person who smokes or uses other forms of tobacco are often a sign of lung damage or irritation of the throat or esophagus.
Nonproductive coughs
A nonproductive cough is dry. It doesn't produce sputum. A dry, hacking cough may occur toward the end of a cold or after exposure to an irritant, such as dust or smoke. There are many causes of a nonproductive cough. They include:
- Viral illnesses. After a common cold, a dry cough may last several weeks longer than other symptoms. It often gets worse at night.
- Bronchospasm. A nonproductive cough, particularly at night, may mean spasms in the bronchial tubes caused by irritation.
- Allergies. Frequent sneezing is also a common symptom of allergic rhinitis.
- Medicines called ACE inhibitors.
- Exposure to dust, fumes, and chemicals in the workplace.
- Asthma. A chronic dry cough may be a sign of mild asthma. Other symptoms may include wheezing, shortness of breath, or a feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Blockage of the airway by an inhaled object, such as food or a pill.
Antibiotic use
Many coughs are caused by a viral illness. Antibiotics aren't used to treat viral illnesses. They don't change the course of viral infections. Using an antibiotic when you don't need it exposes you to the risks of an allergic reaction and antibiotic side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rashes, and yeast infections. Antibiotics also may kill helpful bacteria and encourage the growth of dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Temperature varies a little depending on how you measure it. For adults and children age 12 and older, these are the ranges for high, moderate, and mild, according to how you took the temperature.
Oral (by mouth) temperature
- High: 104°F (40°C) and higher
- Moderate: 100.4°F (38°C) to 103.9°F (39.9°C)
- Mild: 100.3°F (37.9°C) and lower
A forehead (temporal) scanner is usually 0.5°F (0.3°C) to 1°F (0.6°C) lower than an oral temperature.
Ear temperature
- High: 105°F (40.6°C) and higher
- Moderate: 101.4°F (38.6°C) to 104.9°F (40.5°C)
- Mild: 101.3°F (38.5°C) and lower
Armpit (axillary) temperature
- High: 103°F (39.5°C) and higher
- Moderate: 99.4°F (37.4°C) to 102.9°F (39.4°C)
- Mild: 99.3°F (37.3°C) and lower
If you're not sure if a fever is high, moderate, or mild, think about these issues:
With a high fever:
- You feel very hot.
- It is likely one of the highest fevers you've ever had. High fevers are not that common, especially in adults.
With a moderate fever:
- You feel warm or hot.
- You know you have a fever.
With a mild fever:
- You may feel a little warm.
- You think you might have a fever, but you're not sure.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Symptoms of difficulty breathing can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel a little out of breath but still be able to talk (mild difficulty breathing), or you may be so out of breath that you cannot talk at all (severe difficulty breathing).
- It may be getting hard to breathe with activity (mild difficulty breathing), or you may have to work very hard to breathe even when you're at rest (severe difficulty breathing).
Severe trouble breathing means:
- You cannot talk at all.
- You have to work very hard to breathe.
- You feel like you can't get enough air.
- You do not feel alert or cannot think clearly.
Moderate trouble breathing means:
- It's hard to talk in full sentences.
- It's hard to breathe with activity.
Mild trouble breathing means:
- You feel a little out of breath but can still talk.
- It's becoming hard to breathe with activity.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Symptoms of serious illness may include:
- A severe headache.
- A stiff neck.
- Mental changes, such as feeling confused or much less alert.
- Extreme fatigue (to the point where it's hard for you to function).
- Shaking chills.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Self-Care
Coughing is your body's way of removing foreign substances and mucus from your lungs and upper airway passages. Productive coughs are often useful. Don't try to stop a productive cough. Sometimes, though, coughs are severe enough to impair breathing or prevent rest. Here are some things you can do at home to help you feel more comfortable when you have a cough.
- Prevent dehydration.
Fluids may help thin mucus and soothe an irritated throat. Honey or lemon juice in hot water or tea may help a dry, hacking cough.
- Gargle.
Try gargling with warm salt water to help ease a sore throat caused by coughing.
- Prop up your head with extra pillows at night.
This can help ease a dry cough.
- Try a cough drop to soothe an irritated throat.
Medicine-flavored cough drops are no better than candy-flavored drops or hard candy. Most cough drops have no effect on the cough-producing process.
- Try moist air.
Try a vaporizer or humidifier to add moisture to the room. Warm or cool mist may help relieve symptoms. Follow all cleaning instructions and precautions for the machine.
- Stay away from tobacco.
- Don't smoke or use other forms of tobacco, especially while you have a cough.
- Avoid exposure to inhaled irritants.
- Stay away from smoke, dust, and other pollutants.
- Wear a face mask that is the right kind for the exposure. Many kinds of face masks are available. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to find out which type of face mask will help most.
- Think about using cough medicine, which may help your cough.
Avoid cold remedies that combine medicines to treat many symptoms. In most cases, it's better to treat each symptom separately. There are two kinds of cough medicines: expectorants and suppressants.
- Try an expectorant for a productive cough.
- Expectorants thin mucus. They make it easier to cough up mucus when you have a productive cough.
- Use an expectorant if you have a cough that produces thick mucus and you are having trouble coughing up the mucus.
- Don't use just an expectorant to thin the mucus. Drink plenty of water too.
- Try a cough suppressant for a dry, hacking cough that keeps you awake.
- Use cough suppressants such as Delsym, Mucinex DM, or Robitussin wisely. Don't suppress a productive cough too much, unless it's keeping you from getting enough rest. Coughing is useful. It brings up mucus from the lungs and helps prevent bacterial infections. People with asthma and other lung diseases need to cough.
- If an over-the-counter medicine doesn't help, ask your doctor if there is another cough suppressant you can try.
- Be aware of cough medicine precautions.
- Read the package carefully or ask your pharmacist or doctor to help you choose a cough medicine. These medicines can cause problems for people with other health problems, such as asthma, heart failure, high blood pressure, glaucoma, or an enlarged prostate. They may also interact with other medicines, such as sedatives and certain antidepressants.
- Read the label so you know what ingredients you are taking. Some cough medicines contain a large percentage of alcohol. Others contain codeine. Don't give codeine to children younger than age 18. There are many choices. Ask your pharmacist to advise you.
- Use cough medicines with caution if you are older than 60 or if you have chronic breathing problems.
- Keep them out of the reach of children to prevent accidental use.
- Don't take someone else's prescription cough medicine.
- Watch how much you use. Some of these medicines can cause problems if you use too much.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse trouble breathing.
- A fever.
- Coughing up blood.
- Coughing up yellow or green mucus.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.