Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Condition Basics
What is diabetic retinopathy?
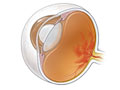
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition caused by diabetes. Diabetes can damage small blood vessels in part of your eye. This can lead to poor vision and blindness.
What causes it?
Diabetes damages small blood vessels throughout the body. Diabetic retinopathy happens when prolonged high blood sugar damages the blood vessels of the retina. This is the part of the eye that sends images to your brain. Other conditions that increase your risk include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and kidney disease.
What are the symptoms?
There are usually no symptoms of diabetic retinopathy until it starts to change your vision. When this happens, the disease is already severe. Changes in vision can be a sign of severe damage to your eye. These changes can include floaters, pain in the eye, blurry vision, or new vision loss.
How is it diagnosed?
An eye exam by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist) is the only way to find diabetic retinopathy. Having a dilated eye exam regularly can help find retinopathy before it changes your vision. On your own, you may not notice symptoms until the disease is severe.
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
Treatment can't cure diabetic retinopathy. But it can help prevent, delay, or reduce vision loss. Treatment includes laser treatment, medicine, or surgery. You may need to be treated more than once. Keeping your blood sugar in your target range is important. This can help keep the condition from getting worse.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Symptoms
There are usually no symptoms of diabetic retinopathy until it starts to change your vision. When this happens, the disease is already severe. Having your eyes checked regularly can find the disease early enough to treat it. Treatment can help prevent vision loss.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy and its complications may include:
- Blurred or distorted vision or trouble reading.
- Floaters or spots in your vision.
- Partial or total loss of vision. Or you might have a shadow or veil across your field of vision.
- Pain, pressure, or constant redness of the eye.
What Happens
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to poor vision and even blindness. It often gets worse over many years.
At first, the blood vessels in the eye get weak. Blood and other liquid can leak into the retina from the blood vessels. If the fluid leaks into the center of your eye, you may have blurry vision.
If blood sugar levels stay high, the condition will keep getting worse. New blood vessels grow on the retina. These blood vessels can break open easily. If they break open, blood can leak into your eye and change your vision. This bleeding can also cause the retina to move away from the wall of the eye (retinal detachment). Sometimes people don't have symptoms until it's too late to treat them. That's why regular eye exams are important.
Retinopathy can also cause swelling in the middle of the retina (macula). This is called macular edema.
Learn more
When to Call a Doctor
Call your doctor now if you have diabetes and notice:
- New or sudden vision changes.
- Floaters in your field of vision. Floaters often appear as dark specks, globs, strings, or dots. A sudden shower of floaters may be a sign of a retinal detachment, which is a serious complication of diabetic retinopathy.
- A new visual defect, shadow, or curtain across part of your vision. This is another sign of retinal detachment.
- Eye pain or a feeling of pressure in your eye.
- New or sudden vision loss. Sudden partial or complete vision loss is a symptom of many disorders that can occur within or outside the eye, including retinal detachment or bleeding within the eye. Sudden vision loss is always a medical emergency.
Call your doctor for an appointment if:
- You have more and more trouble doing everyday tasks (like driving or reading) because of your eyesight.
Watchful waiting
Watchful waiting is not okay if you have diabetes and notice changes in your vision.
If you have type 2 diabetes, even if you don't have any symptoms of eye disease, you still need to have your eyes and vision checked regularly by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist). If you wait until you have symptoms, it's more likely that complications and severe damage to the retina will have already happened. These may be harder to treat. You could end up with permanent vision loss.
If you have type 1 diabetes, are age 10 or older, and were diagnosed 5 or more years ago, you should have your eyes checked even if you don't have symptoms. If you wait until you have symptoms, it's more likely that complications and severe damage to the retina will have happened. These may be harder to treat. And the damage may be permanent.
Watchful waiting is not an option if you already have diabetic retinopathy but don't have symptoms or vision loss. You will need to go back to your ophthalmologist for frequent checkups (every few months in some cases) so that your doctor can closely monitor changes in your eyes. There is no cure for the disease. But treatment can slow its progression. Your ophthalmologist can tell you how often you need to be checked.
Exams and Tests
Diabetic retinopathy can be found during a dilated eye exam. This exam is done by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. An exam by your primary doctor, when your eyes aren't dilated, isn't the same. You need a full exam done by an ophthalmologist or optometrist.
Eye exams for people with diabetes can include:
- Visual acuity testing. This measures how well your eye can focus. It also checks how well you can see details at near and far distances.
- Ophthalmoscopy and slit lamp exam. These may be used to find clouding of the lens (cataract), changes in the retina, and other problems.
- Tonometry. This test measures the pressure inside the eye. It is used to help find glaucoma.
Regular dilated eye exams can help find eye diseases early. And they can prevent or delay vision loss.
Screening for diabetic retinopathy
If diabetic retinopathy hasn't been diagnosed, the American Diabetes Association recommends that:footnote 1
- People with type 1 diabetes who are age 10 and older should have a dilated eye exam within 5 years after diabetes is diagnosed. Then they should be tested every year.
- People with type 2 diabetes should have an exam as soon as diabetes is diagnosed. Then they should be tested every year.
- People who have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and who are planning to become pregnant should have an exam before they get pregnant, if they can. They should have an exam once during the first 3 months (first trimester) of pregnancy. Further screening depends on the results of these tests.
If your eye exam results are normal, you may need fewer follow-up exams.
People who are pregnant and have gestational diabetes aren't at risk for diabetic retinopathy. They don't need to be screened for it.
Learn more
Treatment Overview
There's no cure for diabetic retinopathy. But treatment often works very well to prevent, delay, or reduce vision loss. The earlier retinopathy is found, the easier it is to treat. And it's more likely that vision will be saved.
Treatment options include:
- Laser treatment (photocoagulation).
This usually works very well to prevent vision loss if it's done before the retina has been severely damaged.
- Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) or an anti-inflammatory medicine.
Sometimes injections of these types of medicine can help to shrink new blood vessels when diabetic retinopathy is advanced.
- Surgical removal of the vitreous gel (vitrectomy).
This may help improve vision if the retina hasn't been severely damaged.
Keeping your blood sugar levels within your target range can help keep eye problems from getting worse.
Many people with retinopathy need to be treated more than once as the condition gets worse.
Learn more
Self-Care
Taking care of yourself
- Have regular eye exams. Tell your doctor about any changes in your vision.
- Keep your blood sugar in your target range.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods, and follow your meal plan so you know how much carbohydrate you need for meals and snacks.
- Stay as active as you can. For many people, walking is a good choice. Bit by bit, increase the amount you are active every day. Try for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week.
- Be safe with medicines. Take your medicine exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine.
- Check your blood sugar as often as your doctor recommends.
- Eat a low-salt diet. If you have high blood pressure, this may help lower it. You may also need to take medicines to reach your goals.
- If you smoke, quit or cut back as much as you can. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
- Avoid risky activities. These include things like weight lifting and some contact sports. They may trigger bleeding in the eye through impact or increased pressure.
- Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or planning to get pregnant. Retinopathy can get much worse during pregnancy. Planning ahead with your doctor and following the doctor's instructions can decrease this risk.
Learn more
Related Information
References
Citations
Credits
Current as of: July 7, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 7, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.